
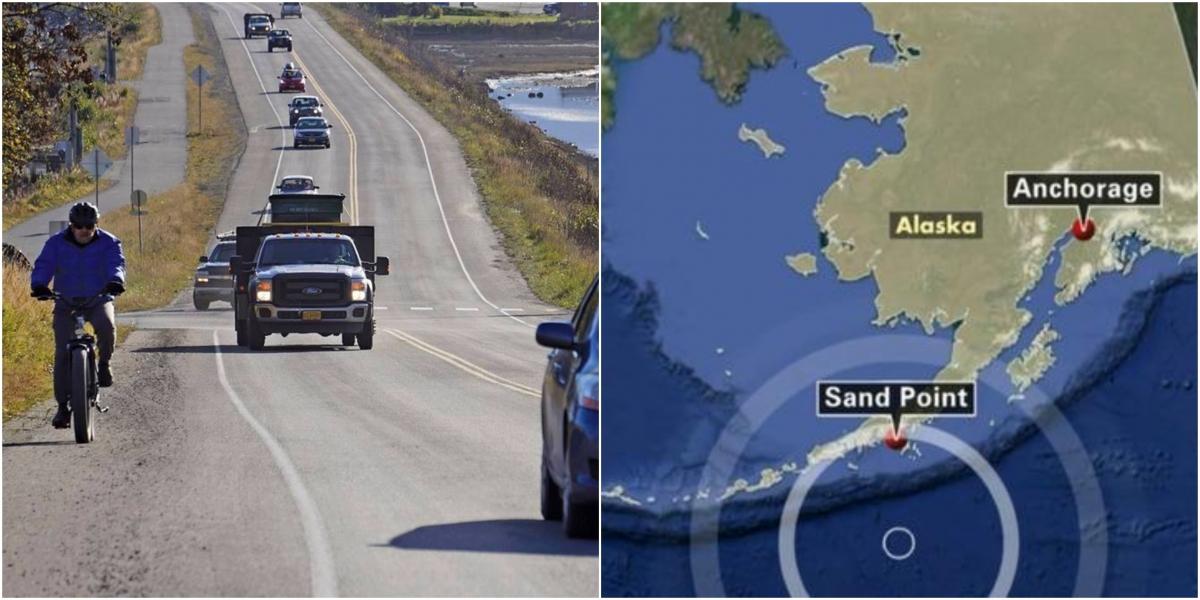
history, tied with another Alaskan quake from 1938, according to USGS data. The quake was the seventh largest in U.S. In Sand Point, which also evacuated on Wednesday night, morning checks revealed no road, harbor or dock damage, said Jordan Keeler, administrator for the community of about 1,300 people.Īccording to the USGS, the quake was followed by over 25 aftershocks in the region, with two around magnitude 6.0. "It makes it more likely that something is going to happen adjacent." "When that happens next to an area that's still locked, it increases the stress in the adjacent area," he said. That temblor appears to have helped set up Wednesday’s quake, Holtkamp said, a typical phenomenon when a big event strikes a major fault or subduction zone, he said. Holtkamp said Wednesday's earthquake was likely related to another powerful earthquake in the same area almost exactly a year ago, the Magnitude-7.6 Simeonof Island Earthquake of July 21, 2020, which struck about 45 miles (72 km) away. That particular section of the subduction zone, called the Aleutian megathrust, is a seismic hot spot, with thousands of earthquakes each year, according to the Alaska Earthquake Center. Wednesday's earthquake struck along a subduction zone where the Pacific plate dives under the North American plate, Holtkamp said. "Even if you were right on top of the earthquake, you'd still be 30 kilometers away from it because it was so deep," said Holtkamp, who works for the Alaska Earthquake Center at the University of Alaska Fairbanks. Vehicles evacuate Homer Spit following tsunami warning after a quake, in Homer, Alaska, U.S., Jin this still image obtained from a video on July 29, 2021. In Alaska, small tsunami waves measuring under a foot (30 cm) above tide level were observed in Sand Point, Old Harbor, King Cove, Kodiak, Unalaska and Alitak Bay, according to the U.S. Wednesday's earthquake triggered a tsunami warning and evacuations in several Alaska coastal communities. It struck about 65 miles (105 km)southeast of Perryville, about 500 miles (800 km) from Anchorage, Alaska's biggest city. Geological Survey (USGS) said the quake was at a depth of 20 miles (32 km). "I'm pretty sure there's some damage around, but we haven't checked." "Stuff fell down and all," said Alec Phillips of the Native Village of Perryville, the tribal government in the community closest to the earthquake. Cool colors represent deep earthquakes and warm colors represent shallow earthquakes. Among them was Seward on the Kenai Peninsula, south of Anchorage, where sirens blared and residents were told to move to higher ground.īut residents of affected communities said they were still assessing impacts after their late-night evacuations to higher ground. On average, Alaska has had one M 8+ earthquake every 13 years.
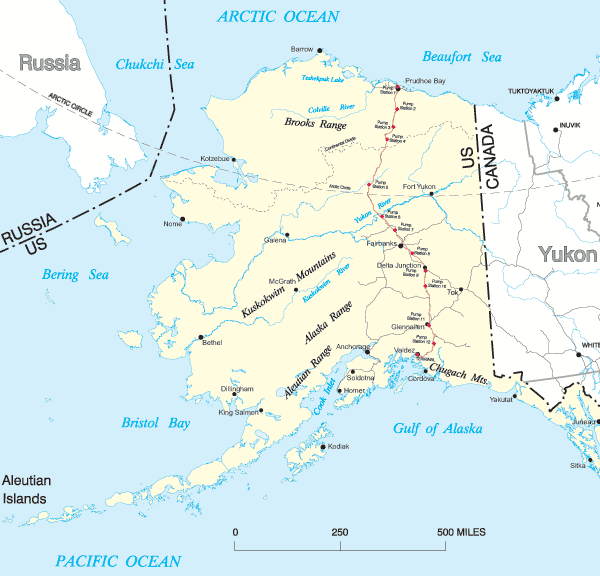
Several Alaskan coastal communities were evacuated following the quake. There were no immediate reports of injuries or damage to property. local time on Wednesday (0615 GMT Thursday) just off the Aleutians, was the strongest felt in the United States since an 8.7 quake ripped through the western Aleutian Islands in 1965. The magnitude-8.2 Chignik Earthquake, which struck at 10:15 p.m. earthquake in half a century left Alaska mostly unscathed, thanks to the remote location and depth of the epicenter, officials said on Thursday.

since a magnitude 8.7 earthquake in the Aleutians in 1965.ANCHORAGE, Alaska, July 29 (Reuters) - The most powerful U.S.

The earthquake center at the time said it was the biggest quake in the U.S. It was widely felt but caused no major damage in the sparsely populated region closest to it. The epicenter, with a depth of 32.2 km, was determined to be at 55.325 degrees north latitude and 157.841 degrees west longitude. The two 6.9 quakes were the largest aftershocks tallied since the United States experienced its largest earthquake in the past half-century, the magnitude 8.2 quake that struck south of the Alaska Peninsula on July 28. SAN FRANCISCO, July 29 (Xinhua) - An earthquake with a magnitude of 8.2 jolted 104 km southeast of Perryville, Alaska at 0615 GMT on Thursday, the U.S. Geological Survey on Twitter had reported a preliminary magnitude of 6.5 that was later revised to 6.9, which ties another earthquake that hit Alaska in August. Jeremy Zidek, a spokesperson for Alaska’s emergency management office, said the office was contacting communities and had no reports of damage so far. The center had not received reports of significant damage but also relies on self-reporting, said seismologist Natalia Ruppert. For more info & to submit a DYFI report, pls go to /qWzbtB6wkd- Alaska Earthquake Center October 11, 2021 It is an aftershock of the M8.2 Chignik EQ, & was felt along the AK Peninsula & Kodiak Island. This event is 71 miles E of Chignik, at a depth of 43 miles. We have reviewed a M6.9 EQ on Oct 11, at 1:10 AM.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
